ClinOleic
An olive oil-based lipid emulsion that is associated with fewer infections than soybean oil and may preserve immune function.1-4

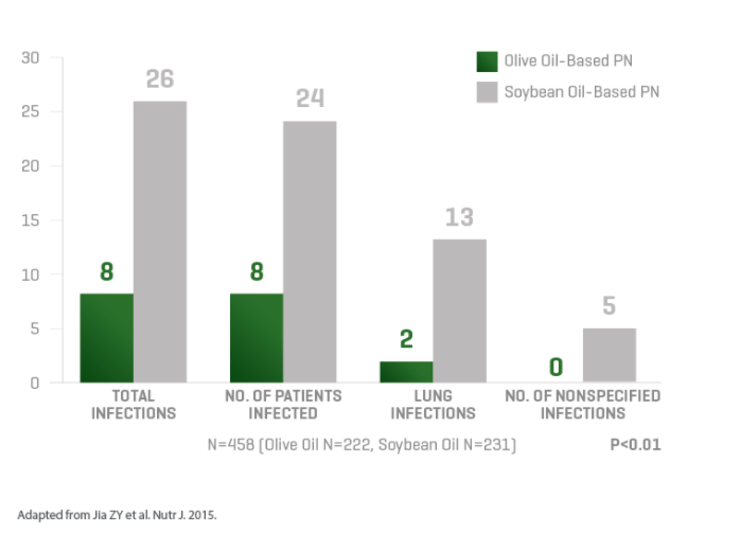
Lipids are an integral part of parenteral nutrition (PN), but some lipid emulsions, such as 100% soybean oil, may modulate patient immune response and increase the risk of complications.3,5 Through 20 years of experience, ClinOleic maintains the lowest soybean oil content of any soy-containing composite lipid emulsion.6-11 ClinOleic also contains 80% olive oil, which has been associated with fewer infections and may preserve immune function.1-4

Aligned with international guidelines
ASPEN guidelines recommend to withhold or limit soybean oil-based lipid emulsions during the first week following the initiation of PN.18 Additionally, ESPEN guidelines recommend that lipids based solely on soybean oil be avoided.14 ClinOleic has the lowest soybean oil content of any soy-containing composite lipid product on the market, enabling the delivery of essential fatty acids while minimizing the unwanted effects of soybean oil.6-11,15
Learn more about Clinical Nutrition

Related Products
CLINOLEIC 20% 100 ml classe C Prezzo al pubblico a confezione con IVA 662,13€
CLINOLEIC 20% 250 ml classe C Prezzo al pubblico a confezione con IVA 653,61€
CLINOLEIC 20% 500 ml classe C Prezzo al pubblico a confezione con IVA 594,20€
CLINOLEIC 20% 1000 ml classe C Prezzo al pubblico a confezione con IVA 534,78€